
One of the strongest advantages of Adaptive Noise Reduction is that it can work in real time while you’re playing your audio. If you want to make changes, Adaptive Noise Reduction shows up in the effects rack when you’re in the multitrack view. A higher number is better for sustained noise like a hum while a low number is better for isolated noise like clicks and pops. FFT Size-This setting adjusts how many frequency bands are analyzed.Lower Broadband Preservation settings will remove more noise, but might introduce audible changes to your project. Broadband Preservation-This slider prevents Adaptive Noise Reduction from altering frequencies above or below any detected noise.Spectral Decay Rate-You want to fine tune this slider to improve how quickly noise reduction drops the Db of detected noise-it helps clean up the final audio.


The higher this number goes, the more likely you are to damage the audio you want to keep. Reduce Noise By-This sets the amount of reduction that the noise remover effect does.Here’s a quick breakdown of what each of these sliders changes. The various sliders that pop up when you open the Adaptive Noise Reduction tool allow you to adjust the noise reduction. You can find the Adaptive Noise Reduction effect by navigating Effects > Noise Reduction / Restoration > Adaptive Noise Reduction.
#Capture noise print audition how to#
How to use Adobe Audition (Beginner’s Guide)Īdaptive Noise Reduction is similar to the standard Noise Reduction, but it works in the effects rack rather than in the waveform editor.I recommend playing around with the sliders until you’ve removed your annoying noise without damaging the audio you want to keep. The two sliders on the bottom adjust the amount of noise that the effect removes from your audio.
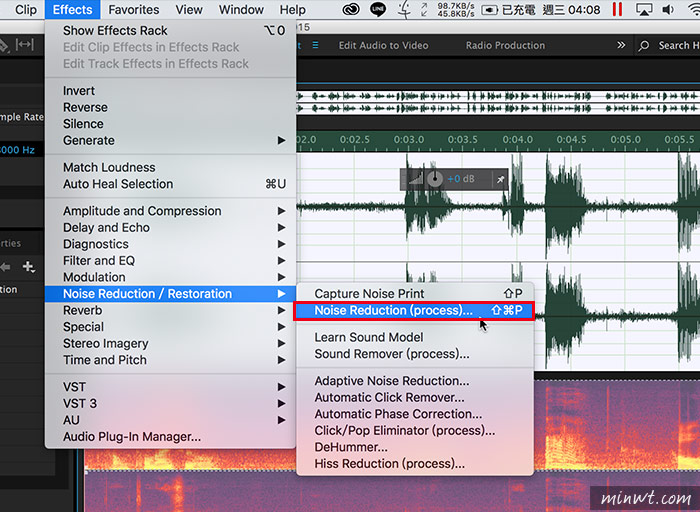
This will open up the controls for the noise reduction effect. Background voices and the audio you want to keep are incredibly similar which means this Noise Reduction effect might do more damage to your audio than it’s worth. If your noise print contains sounds similar to those you want to keep, it might not work.Ī good example of this is removing unwanted voices from the background of podcast audio. This way of removing noise is heavily dependent on capturing a good noise print. You can also navigate to Effects > Noise Reduction / Restoration > Noise Reduction (process). The easiest way to pop up the Noise Reduction options is to use the keyboard shortcut Command+Shift+P on a Mac, or Windows+Shift+P on PC. The Noise Reduction menu also has a one-button “capture noise print” option.
#Capture noise print audition mac#
You can create a noise print by highlighting a section of audio and hitting Shift+P on a Mac or Windows. Noise Reduction will not work until you capture a noise print. I’ve got one noisy recording to work with for this guide on how to remove background noise Adobe Audition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
